Document Translation
Your Asian language experts.
Many of our clients find it difficult to decide which Chinese dialect to use. One of the questions that often come up is whether Hong Kong Traditional Chinese is the same as Taiwanese Traditional Chinese? Furthermore, mistakes are often made when specifying Cantonese as a target language. So, what are the differences between these languages? You may find this table helpful:
| Country | Oral | Written |
|---|---|---|
| Mainland China | Mandarin | Simplified Chinese |
| Hong Kong SAR | Cantonese | Traditional Chinese |
| Taiwan | Mandarin | Traditional Chinese |
| Singapore | Mandarin | Simplified Chinese |
From the above chart, you can see that people in Mainland China and Taiwan speak Mandarin but the written scripts they use are different. This is explained by the fact that Mainland China and Taiwan have different governments, and several decades ago, the government of Mainland China started advocating Simplified Chinese to improve handwriting efficiency (Simplified Chinese characters have fewer strokes). As such, the same character is written differently in Mainland China and Taiwan.
Besides this major difference, as we all know, language is constantly evolving, and this evolution will create differences after some time. Such differences are particularly evident in the IT field. This is because the terms in this field were defined by a different group of experts in Mainland China and Taiwan, and most of these terms were created after the 1970s, i.e. long after the Chinese civil war (which caused the separation today).
The written scripts of Hong Kong SAR and Mainland China are also different for similar reasons, except that before the handover in 1997, Hong Kong was under British rule instead of the Chinese government. Hong Kong SAR, however, shares the same spoken language – Cantonese – as Guangdong Province of China. It is incorrect to request Cantonese as a written target language because 1) it is not a written language; and 2) Guangdong Province speaks Cantonese, but the written language used there is Simplified Chinese, not Traditional Chinese (which is used in Hong Kong).
As seen in the chart, the written scripts used in Taiwan and Hong Kong SAR are both Traditional Chinese. However, they are not completely the same. This is because people from Hong Kong adopted terms from both Mainland China and Taiwan, and also have some terms defined by themselves.
To make sure your project is translated into the correct target language, it is important for you to know the target market. You should always indicate a target language as shown below:
“Simplified Chinese for Mainland China”
“Simplified Chinese for Mainland China”
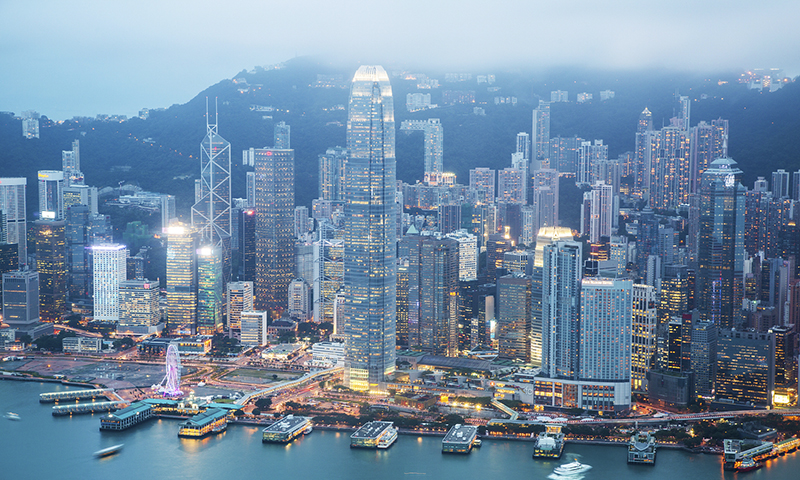

“Traditional Chinese for Hong Kong”
“Traditional Chinese for Hong Kong”
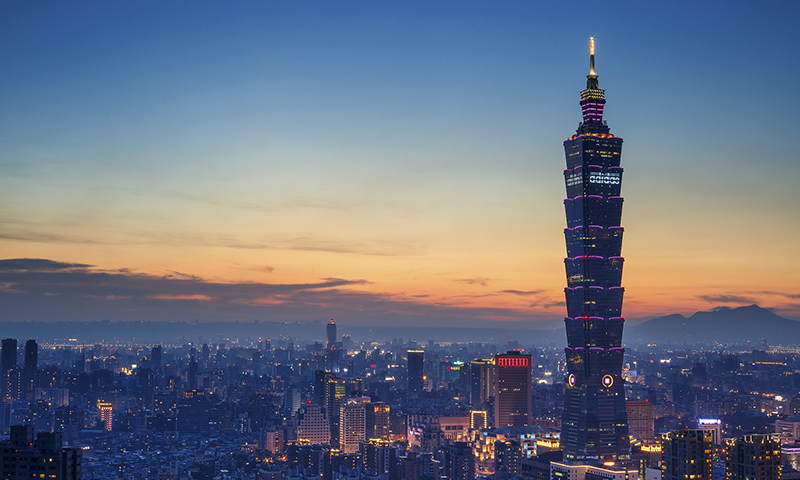

“Traditional Chinese for Taiwan”
“Traditional Chinese for Taiwan”
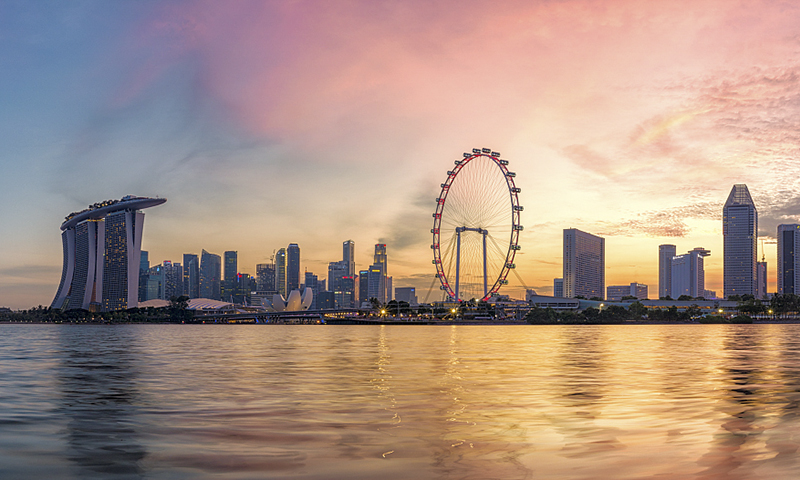

“Simplified Chinese for Singapore”
“Simplified Chinese for Singapore”